Email Harvesting
In cybersecurity, Email Harvesting refers to collecting email addresses from various sources, including websites, social media platforms, online directories, forums, and other publicly accessible sources. Email harvesting can be conducted manually by individuals or automated using specialized software tools or scripts.
It is essential to measure an organization's external susceptibility to Email Harvesting for several reasons:
Phishing Attacks: Email harvesting provides attackers with a list of valid email addresses that can be targeted in phishing attacks. By sending phishing emails to harvested email addresses, attackers trick recipients into disclosing sensitive information, clicking on malicious links, or downloading malware. Measuring susceptibility to Email Harvesting helps organizations assess the risk of phishing attacks and implement appropriate safeguards to protect against them.
Spamming: Harvested email addresses can send unsolicited bulk emails (spam) promoting products, services, or malicious content. Spam emails can overwhelm email servers, disrupt business operations, and decrease employee productivity. Measuring susceptibility to Email Harvesting helps organizations identify potential sources of spam emails and implement spam filtering solutions to reduce the impact on their email infrastructure.
Social Engineering: Email harvesting can be used in social engineering attacks to gather information about individuals or organizations for targeted attacks. Attackers may use harvested email addresses to impersonate trusted entities, gain recipients' trust, and manipulate them into divulging confidential information or performing unauthorized actions. Measuring susceptibility to Email Harvesting helps organizations identify and mitigate the risk of social engineering attacks targeting their employees, customers, or partners.
Data Privacy and Compliance: Email harvesting raises concerns about data privacy and compliance with regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Organizations may inadvertently expose email addresses of customers, employees, or partners through websites, online forms, or public directories, leading to potential violations of data protection laws. Measuring susceptibility to Email Harvesting helps organizations identify and address vulnerabilities in their data handling practices to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and protect sensitive information.
Reputation Management: Email harvesting can damage an organization's reputation and erode customer, partner, and stakeholder trust. If email addresses are harvested from public sources without consent, recipients may perceive the organization as careless with their personal information, losing confidence and credibility. Measuring susceptibility to Email Harvesting helps organizations implement measures to protect against unauthorized data collection and demonstrate a commitment to safeguarding privacy and security.
Measuring an organization's external susceptibility to Email Harvesting is essential for identifying security risks, assessing the potential impact of cyber threats, and implementing proactive measures to protect against phishing attacks, spam, social engineering, data privacy violations, and reputational damage. By implementing adequate email security controls and measures, organizations can mitigate the risk of email harvesting and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure
ThreatNG significantly enhances an organization's defense against email harvesting through its robust and comprehensive capabilities:
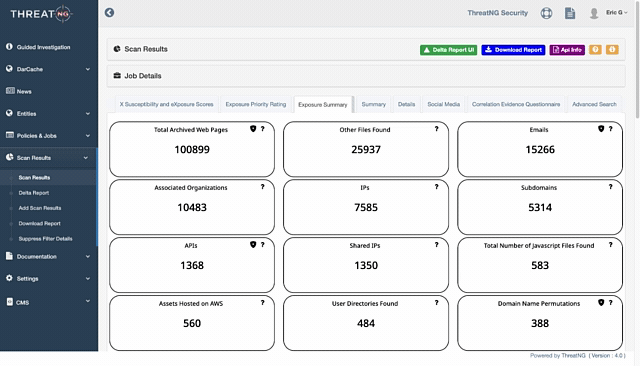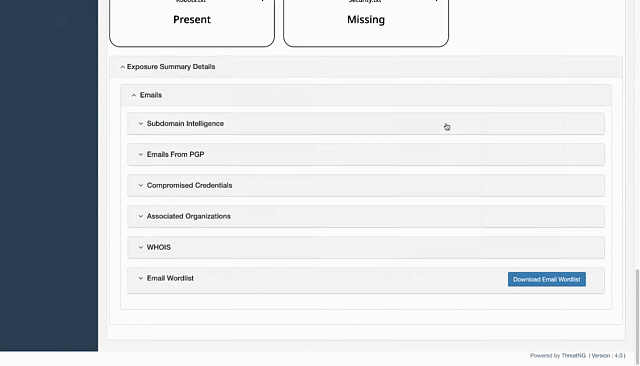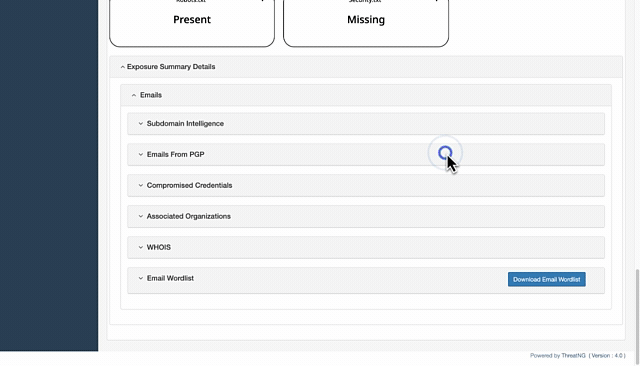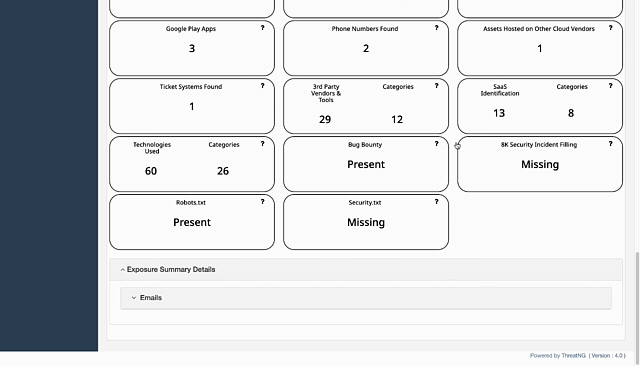
Comprehensive Discovery: ThreatNG excels at identifying exposed email addresses across various sources.
Its Domain Intelligence module, with its Email Intelligence capabilities, plays a crucial role by providing email security presence and format prediction and also offering harvested emails.
Search Engine Exploitation helps uncover email addresses that may be inadvertently exposed through search engine results.
The platform's ability to analyze Cloud and SaaS Exposure can reveal email addresses stored in cloud-based applications or services.
Online Sharing Exposure scans platforms like Pastebin and GitHub Gist, where email addresses might be shared or leaked.
Furthermore, ThreatNG's Archived Web Pages analysis can uncover email addresses in older versions of websites or documents.
This multi-faceted discovery provides a comprehensive view of where an organization's email addresses are vulnerable to harvesting.
Risk Assessment and Prioritization: ThreatNG doesn't just find emails; it helps assess the risk associated with their exposure.
The Cyber Risk Exposure module considers various factors to determine the potential impact of email harvesting, including the sensitivity of the exposed data and the presence of vulnerabilities.
Additionally, ThreatNG's BEC & Phishing Susceptibility assessment, derived partly from Email Intelligence, addresses the risk of email-based attacks.
This enables organizations to prioritize remediation efforts effectively, focusing on the highest-risk exposures.
Proactive Threat Mitigation: ThreatNG's value extends beyond discovery and assessment.
Its continuous monitoring capabilities enable the detection of unusual patterns that might indicate email harvesting activity.
ThreatNG's intelligence can inform rules and policies within those systems.
Collaboration with Existing Solutions: ThreatNG's intelligence complements and enhances existing security tools.
For example, threat intelligence feeds from ThreatNG, containing information about exposed email addresses and harvesting patterns, can be ingested by email security gateways to improve filtering and blocking accuracy.
Real-World Examples:
A financial institution can use ThreatNG to discover employee email addresses exposed on platforms like LinkedIn or in code repositories. By integrating ThreatNG with its security awareness training platform, the institution can educate employees about email harvesting and phishing risks.
A healthcare provider can leverage ThreatNG to identify patient email addresses exposed in unsecured cloud storage services (like a misconfigured S3 bucket) or archived website files. Integrating ThreatNG with their cloud security solution allows them to enforce stricter access controls, implement encryption, and receive alerts about data exposures.
A government agency can employ ThreatNG to detect attempts to harvest email addresses from its public-facing websites, such as contact forms or employee directories. They can block malicious traffic and prevent unauthorized access by feeding ThreatNG's findings into their web application firewall (WAF) or intrusion prevention system (IPS).
ThreatNG's comprehensive approach to external attack surface management, with its powerful discovery, assessment, and intelligence capabilities, makes it a valuable tool for organizations seeking to proactively defend against email harvesting and a wide range of other cyber threats.